🚀 Kubernetes Starter Guide – A Thread 🧵 Master Kubernetes from scratch with this structured roadmap! 📌 #Kubernetes #DevOps #Cloud
1️⃣ What is Kubernetes? Kubernetes (K8s) is an open-source system for automating deployment, scaling & management of containerized applications. Think of it as an OS for containers! 🔹 Container orchestration 🔹 Handles failures & scaling 🔹 Works on any cloud #Kubernetes101
2️⃣ Kubernetes Architecture 🏗️ Core components: 🔹 Master Node (Control Plane) • API Server • Scheduler • Controller Manager • etcd (Cluster Database) 🔹 Worker Nodes • Kubelet • Kube Proxy • Container Runtime (Docker/Containerd) #Kubernetes #DevOps
3️⃣ Why use Kubernetes? 🤔 ✅ Auto-scaling 🔄 ✅ Load balancing ⚖️ ✅ Self-healing ❤️🔥 ✅ Rolling updates 🚀 ✅ Multi-cloud compatibility ☁️ It helps manage containerized applications efficiently at scale! #CloudNative #Kubernetes
4️⃣ Setup Kubernetes (Locally) 🖥️ 🔹 Minikube – Run Kubernetes on a local machine 🔹 Kind – Lightweight clusters using Docker 🔹 K3s – Lightweight Kubernetes for IoT/Edge 🔹 MicroK8s – Single-node Kubernetes For production, use managed K8s like EKS, GKE, AKS. #KubernetesSetup
5️⃣ Basic Kubernetes Concepts 🔥 📌 Pod – Smallest deployable unit (runs containers) 📌 Node – A worker machine 📌 Deployment – Manages pods & replicas 📌 Service – Exposes pods over a network 📌 ConfigMap & Secret – Store app configs securely #LearnKubernetes
6️⃣ Your First Kubernetes Pod 🚀 Create a simple pod: apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: my-first-pod spec: containers: - name: my-container image: nginx Apply it - kubectl apply -f pod.yaml Verify - kubectl get pods #KubernetesBeginner
7️⃣ Deployments & Scaling ⚡ Define a deployment, apply and scale kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml kubectl scale deployment nginx-deployment --replicas=5
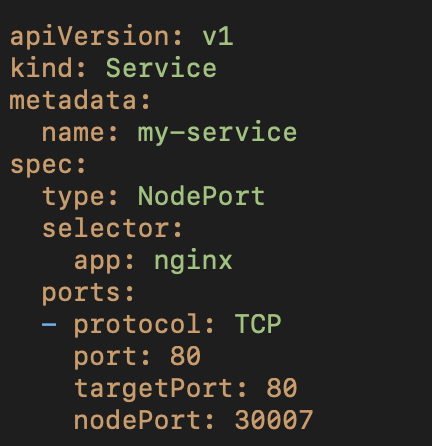
8️⃣ Services: Exposing Your App 🌎 📌 ClusterIP – Internal access only 📌 NodePort – Expose on a port 📌 LoadBalancer – Expose via cloud provider Expose Deployment via NodePort and apply. kubectl apply -f service.yaml kubectl get services #KubernetesNetworking
9️⃣ConfigMaps & Secrets 🔐 📌Store env variables & credentials securely! ConfigMap Eg: apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: appconfig data: ENV: "prod" Secret Eg: apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: dbsecret type: Opaque data: password: cGvcmQ= #base64
🔟 Kubernetes Ingress 🌍 Ingress routes external traffic to services. Example using Nginx Ingress Controller, Apply & access via DNS. #KubernetesIngress
1️⃣1️⃣ Stateful Apps with Kubernetes 📦 Use Persistent Volumes (PV) & Persistent Volume Claims (PVC) to store data persistently. Example:
1️⃣2️⃣ Monitoring & Logging 📊 🔹 Prometheus – Metrics collection 🔹 Grafana – Data visualization 🔹 Fluentd – Log forwarding 🔹 Loki – Log aggregation 🔹 ELK Stack – Centralized logging Monitor Kubernetes to keep your cluster healthy! #KubernetesMonitoring
1️⃣3️⃣ Kubernetes RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) 🔐 Restrict access using Roles & RoleBindings. Example Role - Apply it and bind to a user/service account!
1️⃣4️⃣ Helm – Kubernetes Package Manager 🎩 Use Helm charts to deploy apps easily. Install Helm: curl raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main… | bash Deploy Nginx: helm repo add bitnami charts.bitnami.com/bitnami helm install my-nginx bitnami/nginx #Helm #Kubernetes
1️⃣5️⃣ Kubernetes Best Practices ✅ 🔹 Use namespaces for isolation 🔹 Monitor & log everything 🔹 Secure sensitive data with Secrets 🔹 Set resource limits on pods 🔹 Automate deployments with CI/CD 🔹 Use network policies to restrict traffic #KubernetesTips
🚀 Are you Ready to Master Kubernetes? 📌 Bookmark this thread 💾 Save it for reference 🔁 Repost to share with others! Want an advanced Kubernetes guide next? Reply “YES”! 🚀🔥 #Kubernetes #DevOps